You are here
Call Center Infrastructure
The most critical asset of a call center after human resources is its infrastructure.
The infrastructure should allow an outsourcing vendor to maintain multiple applications and systems for multiple clients and should enable rapid deployment and integration. Hence it becomes necessary for an outsourcing vendor to select the right infrastructure and architecture.
Infrastructure requirements of a typical customer service center include the following:
- Telecommunication network
- Hardware
- Software
Telecommunication Network
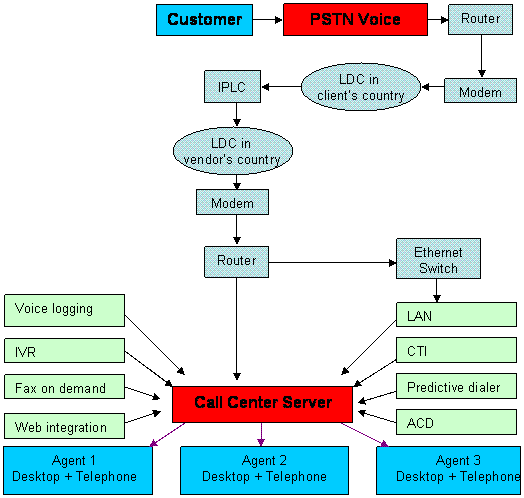
The telecommunication network connects a caller with the agent. The basic elements of a telecommunication network include public switched telephone network (PSTN), router, long distance carrier (LDC), Ethernet switch, modem and contact center server. When the outsourced call center is located in another country, the LDCs in the two regions are connected through the International Private Leased Circuit (IPLC), which is an agreement that provides connectivity through cable or satellite on lease. Companies have recently started using the Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology, which is used to transmit voice, fax and data to another location through Internet Protocol (IP) network.
Hardware
A customer service center should have state of the art hardware components such as local area network (LAN), desktops for agents, automatic call distributor (ACD), predictive dialer, computer technology integration (CTI), Web integration, interactive voice response, fax on demand, and voice logging and messaging. Integration of these different components becomes easy if they have a single platform.
Software
Software is as important as the telecommunication network and hardware in a call center. Various Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software are available that enable an agent to gather information about a customer (who is on line). CRM software also allows segregation of the customers into different types and determining the value of each type. Vendors can use end-to-end CRM software as well as packages catering to specific functions such as telemarketing and technical support, etc.
The telecommunication network and hardware at a typical call center that uses IPLC is given in Figure 1. The client and the customers are generally located in a developed country such as the US and outsourced vendor is located in an offshore destination such as India (Read the report on outsourcing to India for details on India’s value proposition as an offshore destination). The customer connects to a PSTN at the client site. The call is then routed over to LDC in the US. This call is further connected to India through the IPLC between India and the US. The Indian LDC and a local loop transfer the call to the call center server through a router, while the data is transferred to the call center LAN. The ADC distributes the calls to the agents. Other hardware components are used to either obtain information about the customer from the database or to manage the calls efficiently.
Fig 1: "Telecommunication network and hardware in a call center"